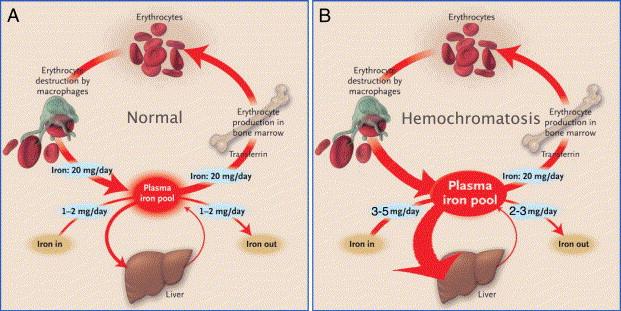
Iron Fist Hemochromatosis, a genetic problem connected with iron digestion, presents extraordinary difficulties that require a nuanced understanding of its underlying genetic variables. This condition, set apart by unnecessary assimilation of dietary iron, can prompt iron over-burden in different organs, possibly causing serious unexpected problems. We should dig into the genetic insights that add to the improvement of iron fist hemochromatosis and how a superior understanding of genetics can inform counteraction and the executives systems.
HFE Quality Changes:
A central member in Iron Fist Hemochromatosis is the HFE quality, situated on chromosome 6. Changes in the HFE quality are the essential genetic component related with the advancement of this problem. The most widely recognized transformations linked to Iron Fist Hemochromatosis are C282Y and H63D.
Inheritance Examples:
Understanding the inheritance examples of Iron Fist Hemochromatosis is vital for assessing an individual’s gamble. This problem follows an autosomal passive example, meaning that an individual should inherit two duplicates of the transformed quality (one from each parent) to foster the condition.
Genetic Screening and Testing:
Genetic screening and testing assume a significant part in identifying individuals in danger for Iron Fist Hemochromatosis. Screening might involve analysing family clinical history and conducting blood tests to survey iron levels.
Preventive Measures:
Understanding the genetic premise of Iron Fist Hemochromatosis takes into consideration designated preventive measures. Individuals with a family background of the issue or those recognized as transporters of HFE quality transformations can take on proactive systems to oversee iron levels.
Individualized Treatment Approaches:
Genetic insights likewise add to the advancement of individualized treatment approaches for Iron Fist Hemochromatosis. While therapeutic phlebotomy is a standard treatment to oversee iron levels, the recurrence and length might differ in light of the genetic profile of the individual. Tailoring treatment to the particular genetic variables involved takes into account more exact and successful administration of the problem.
Understanding the role of genetics in iron fist hemochromatosis is fundamental for early recognition, anticipation, and the executives. The HFE quality changes and their inheritance designs give basic information that guides genetic screening, testing, and the improvement of customized methodologies. With genetic insights, medical care professionals can execute proactive measures to address Iron Fist Hemochromatosis, eventually improving the personal satisfaction for individuals in danger of iron over-burden.